DCM & SyMMES
- Share
- Share on Facebook
- Share on X
- Share on LinkedIn
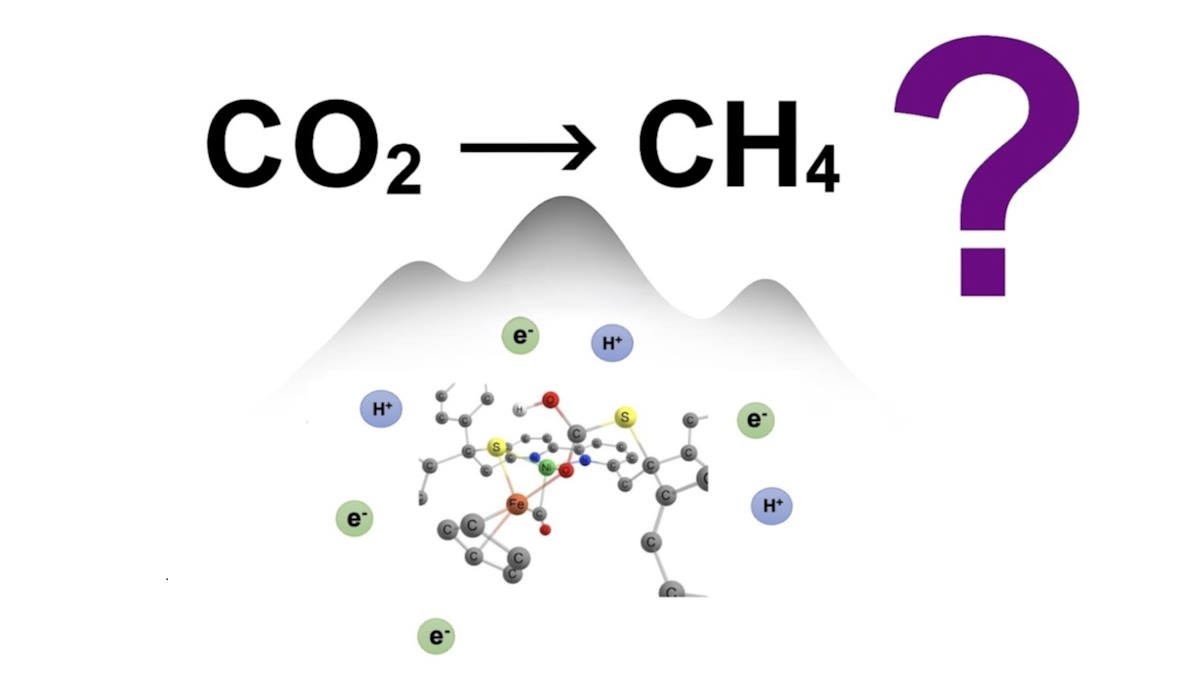
This project aimed at understanding the outstanding catalytic behaviour in CO2 electroreduction of a recently synthesized bioinorganic [NiFe] complex inspired by hydrogenase, thanks to computational methods rooted in Density Functional Theory (DFT). The detailed mechanistic insights obtained here explain the high selectivity of the reduction process yielding CH4 as the sole final product, owing to the cooperativity of the two metal atoms. The findings also highlight the role of the ligand sulfur atoms in binding CO2, as well as the influence of the graphite support experimentally used to enhance electron transfers. Additionally, the modelling disclosed details on the competing H2 evolution reaction and the mechanism of proton relay via a modified [NiFe] complex to improve H2 production.
“Investigating the interplay between charge transfer and CO2 insertion in the adsorption of a NiFe catalyst for CO2 electroreduction on a graphite support through DFT computational approaches”, S. Arjunan, J. M. Sims, C. Duboc, P. Maldivi, A. Milet, J. Comput. Chem. 2024, 45, 1690-1696.
“Tuning the Electronic and Molecular Structures of Bioinspired Heterodinuclear NiFe Catalyst for enhanced Catalytic H2 Evolution”, N. Lalaoui, I. Suarez-Antuna, S. Arjunan, M. Curtil, P. -C. Ioannou, F. Molton, P. Y. Chavant, C. Philouze, A. Milet, P. Maldivi, and C. Duboc, ACS Org. Inorg. Au, 2025, 5, 230-237.
Arcane PhD student
Subash Arjunan
Supervisors
Anne Milet (DCM) & Pascale Maldivi (SyMMES
- Share
- Share on Facebook
- Share on X
- Share on LinkedIn